Gastric Band Surgery
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB), also known as gastric banding or lap band surgery, is a type of bariatric surgery that promotes weight loss by restricting the amount of food that can enter the stomach at any one time. By slowing digestion, it also helps to control feelings of hunger and increase the feeling of fullness after eating a meal. Gastric banding is an alternative that is less invasive and safer than gastric bypass surgery or sleeve gastrectomy.
The gastric band
is the safest type
of bariatric surgery.
Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding does not involve changing the body's natural digestion or cause nutritional deficiencies as with gastric bypass procedures. While the amount of food that can be eaten is restricted, the stomach and intestines are left intact to digest food and nutrients completely and naturally.
About the Procedure

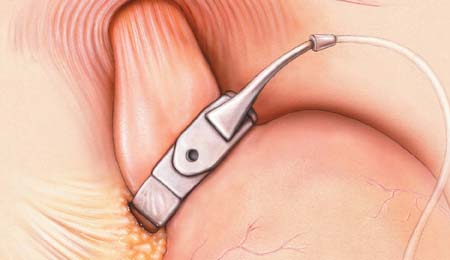
The gastric band is a medical device that is implanted into the body during a relatively quick and minimally invasive operation. It consists of a silicone band lined with inflatable sacs, an injection port, and tubing. The band is placed around the upper stomach and is connected with tubing to an injection port that is attached to the abdominal wall.
There are two gastric bands approved for use in the United States:
- The LAP BAND System
- REALIZE Band (Swedish Adjustable Band)
The inflatable sacs that line the gastric band are usually left empty when first placed into the body. Over time, they are filled with a saline solution to further reduce the opening to the stomach and make it difficult to eat a large amount of food at any one time.
- The adjustability of the gastric band is one of the advantages of this type of bariatric surgery - it can offer personalized weight loss treatment to each patient.
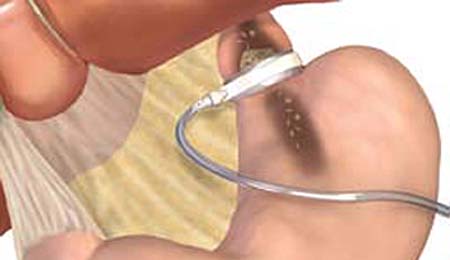
The gastric band fills are performed by a bariatric surgeon on a periodic basis. The saline solution is added to the gastric band using a thin needle that is inserted into the access port. When the saline solution is injected into the port, it travels to the inflatable sacs through the connective tubing and the band tightens around the stomach opening. This shrinks the stomach opening and increases food restriction.
The first fill is often performed about 4 to 6 weeks after surgery. Periodic fills are scheduled over the next couple of years to find the optimal amount of restriction that balances eating comfort with satisfactory weight loss.

Patient Criteria
The gastric band is a specific treatment for obesity and not a general method of weight loss for anyone who is overweight. Certain indications are used as guidelines by bariatric surgeons in determining whether or not an individual is a good candidate for gastric band surgery.
In general, the following guidelines outline patient criteria for gastric banding:
- Individuals with a body mass index (BMI) above 40, or BMI 35 and over with obesity related health conditions (such as high blood pressure, diabetes, sleep apnea), or those who are 100 pounds or more over their ideal weight; (Update: On 2/16/2011, FDA lowered criteria for Lap-Band to include people with BMI of 30 who have at least one related health problem.)
- Individuals between the ages of 18 and 55, although some doctors will accept patients who are either younger or older
- History of obesity (generally at least 5 years)
- History of failed weight loss attempts, including medically supervised weight loss programs
- Individuals who are psychologically stable
- Individuals who are an acceptable operative risk
- Individuals who understand the risks and benefits of the procedure and willing to comply with the lifelong dietary restrictions
Individuals with the following conditions are not good candidates for gastric banding:
- Untreated glandular diseases such as hypothyroidism
- Certain stomach or intestinal disorders such as ulcers, esophagitis, or Crohn's disease
- Severe heart disease or other health conditions that increase operative risks
- Infections
- Undergoing steroid treatment
- Allergies to materials in the band or pain intolerance to implanted devices
- Dependency on alcohol or drugs
- Emotional instability
- Unwilling to follow dietary restrictions
Individuals who are interested in gastric banding should talk to their doctor in order to determine if they are acceptable patients for this bariatric procedure.
The gastric band
can be adjusted
to personalize
weight loss treatment
for each patient.
Advantages of Laparoscopic Adjustable Gastric Banding
- Adjustable - to personalize treatment and rate of weight loss
- Reversible - if medically necessary
- Safe - relatively low operative risk
- Can be unfilled during pregnancy to allow for sufficient nutrition
- Surgery does not involve stomach stapling, cutting and rerouting of the intestine, or bypassing the pyloric valve (normal stomach outlet)
- Laparoscopic surgery allows for quicker recovery, faster healing, less pain, and shorter hospital stay
- Does not cause dumping syndrome
- Does not cause nutritional deficiencies
Possible Complications
Although gastric banding is considered a relatively safe procedure, especially compared to other bariatric surgeries, all surgical procedures involve some degree of risk and possible complications which should be considered before proceeding with surgery. During surgery, complications include: hemorrhage; injury to the spleen, stomach, or esophagus; conversion to open surgery. After surgery, complications include: band slippage, band or tubing leakage; port or band infection; obstruction; nausea and vomiting. Long-term complications include: band erosion into stomach; esophageal dilatation (stretching).
Weight Loss Results
Gastric banding promotes a safe and steady rate of weight loss and long-term weight loss maintenance. The average weight loss in gastric band patients is:
- 1-1/2 to 2 pounds per week
- 50% of excess weight loss in first year
The weight loss also leads to an improvement or resolution of obesity related health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and severe sleep apnea.
- Learn more about the LAP-BAND System.
- Learn more about the REALIZE Band.
- Do you know which foods are problematic and should be avoided on the lap band diet?
Related Articles
Social
Compare!
Each bariatric surgery procedure has its own advantages and disadvantages. Don't choose a procedure based on what is popular at the moment, rather compare the options and decide which one is right for you.